- View Mobile Number
sainathagroindustries@gmail.com
| Business Type | Manufacturer, Exporter, Supplier |
| Sizes available | 8/100 mesh, 16/100 mesh, 30/100 mesh and all customization available |
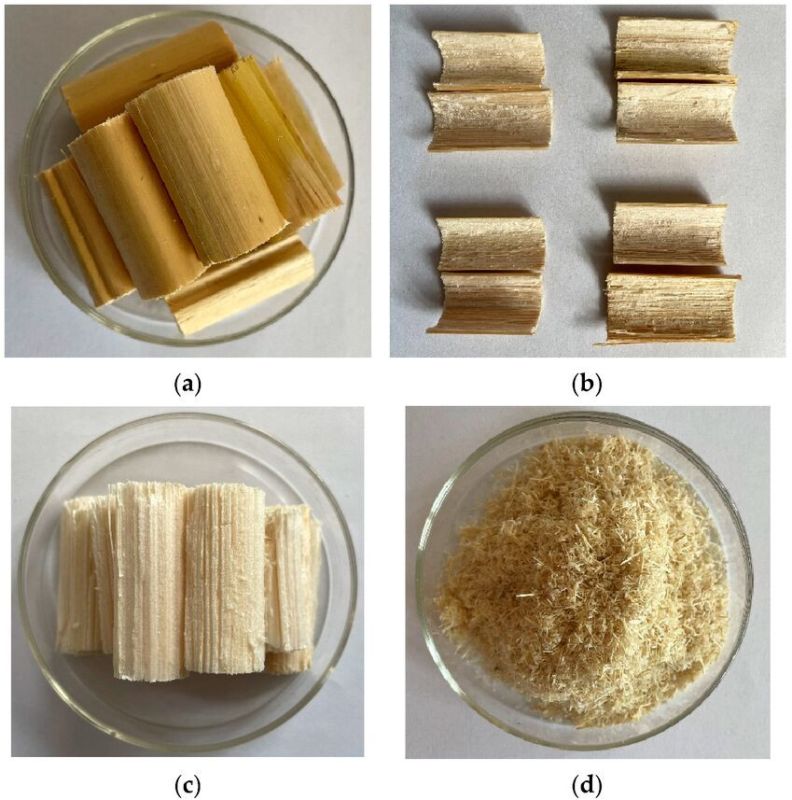
Corn stalk has a high cellulose content, so that it is potential to be used as a composition for making alginate-carboxymethyl cellulose beads. Alginate and cellulose are biodegradable, renewable and nonmeltable polymers that have wide applications in various industrial sectors.
Corn stalk powder uses
Corn stalk powder has a wide range of uses, including as livestock feed, biofuel, and a raw material for paper and building materials. Processing corn stalks into powder is a method of valorizing agricultural waste into high-value products
Agricultural applications
Animal feed
- Feed pellets: Dried and pulverized corn stalks can be pressed into pellets to create feed for cattle, sheep, and other livestock. The pelletization process increases palatability and can kill pathogens.
- Supplementation: Corn stalk powder can be added to cattle rations as a low-cost source of fiber. To increase digestibility and nutritional value, it can be treated with chemicals like calcium oxide or urea before being pelleted.
Soil amendment and fertilizer
- Organic fertilizer: Corn stalks can be fermented with microbial agents to create organic fertilizers. Applying these biofertilizers can enrich soil with vital nutrients such as nitrogen, potassium, and phosphorus
- Mulch and compost: Chipped or powdered corn stalks can be used as a garden mulch to cover the soil and retain moisture. When added to compost, they help create a nutrient-rich soil amendment.
- Soil reclamation: Research shows that applying corn stalk biochar can improve the quality of hostile soils by increasing organic carbon, available nutrients, and water permeability.
Industrial and material production
Biofuels
- Ethanol: The high cellulose content of corn stalk powder makes it a suitable raw material for producing bioethanol, a cleaner-burning fuel alternative.
- Biomass pellets: Torrefied corn stalk pellets can be used as a solid fuel source to replace fossil fuels like coal. These pellets have a high density, which improves their energy efficiency, storage, and transportation.
- Bio-asphalt and bio-oil: Through processes like hydrothermal carbonization, corn stalk-derived hydrochar can be used as a modifier in asphalt pavement, offering improved performance and longevity. Bio-oil can also be produced via liquefaction.
Building and composite materials
- Reinforcing fiber: As a lignocellulosic material, corn stalk powder can be used as a filler or reinforcing agent in composites, such as low-density polyethylene (LDPE).
- Cement replacement: Cornstalk ash, a product of controlled burning, can be used as a partial cement replacement in concrete production.
- Fiberboard and particleboard: The fibrous components of corn stalks can be processed into fiberboard and particleboard, offering a use for waste material.
Paper and cellulose products
- Pulp and paper: Corn stalks contain high levels of cellulose and low levels of lignin, making them a suitable non-wood source for papermaking. Fiber from the stalk is comparable in quality to hardwood.
- Cellulose composites: Cellulose extracted from corn stalk powder can be used as a raw material for various industrial applications, including the creation of biodegradable products.
Environmental remediation
- Biosorbent: Dried corn stalk powder can function as a biosorbent to remove pollutants, such as heavy metals and radioactive iodine, from wastewater. Its chemical properties allow it to bind to contaminants through processes like ion-exchange.
- Animal bedding: Ground corn stalks can serve as an absorbent and natural bedding material for livestock, especially when baled